Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Bounding Ellipsoids
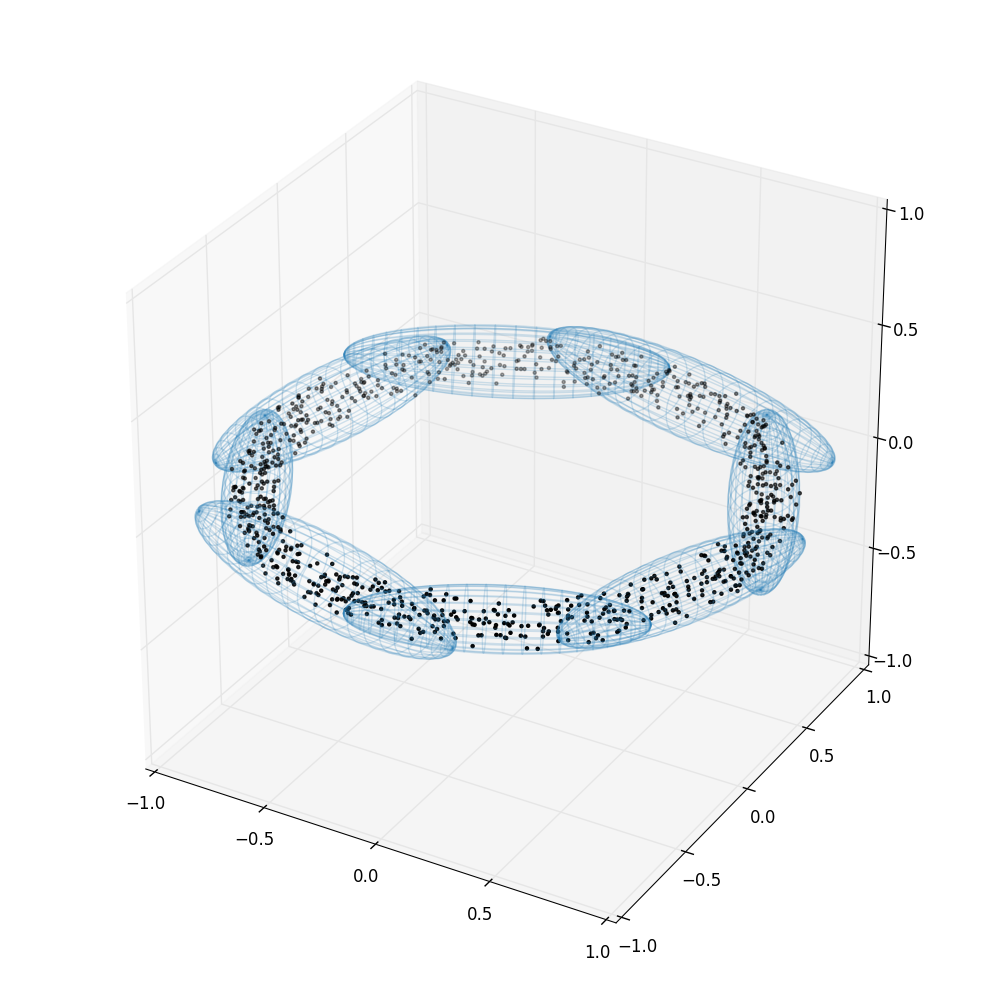
Illustration of determining bounding ellipsoids in 3 dimensions.
For complex iso-likelihood surfaces (ones not well-approximated by a
single ellipsoid), Nestle will bound the points in multiple ellipsoids
when using the 'multi' method. Here, we draw points uniformly
from a torus and use Nestle to determine an optimal set of ellipses
bounding the points.
import math
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import nestle
# seed RNG for reproducible results
np.random.seed(0)
def rand_torus(ro, ri, npoints):
"""Generate points within a torus wth major radius `ro` and minor radius
`ri` via rejection sampling"""
out = np.empty((npoints, 3), dtype=np.float64)
i = 0
while i < npoints:
# generate point within box
x = np.random.uniform(-1., 1., size=3)
x[0:2] *= ro + ri
x[2] *= ri
r = math.sqrt(x[0]**2 + x[1]**2) - ro
if (r**2 + x[2]**2 < ri**2):
out[i, :] = x
i += 1
return out
def plot_ellipsoid_3d(ell, ax):
"""Plot the 3-d Ellipsoid ell on the Axes3D ax."""
# points on unit sphere
u = np.linspace(0.0, 2.0 * np.pi, 100)
v = np.linspace(0.0, np.pi, 100)
z = np.outer(np.cos(u), np.sin(v))
y = np.outer(np.sin(u), np.sin(v))
x = np.outer(np.ones_like(u), np.cos(v))
# transform points to ellipsoid
for i in range(len(x)):
for j in range(len(x)):
x[i,j], y[i,j], z[i,j] = ell.ctr + np.dot(ell.axes,
[x[i,j],y[i,j],z[i,j]])
ax.plot_wireframe(x, y, z, rstride=4, cstride=4, color='#2980b9', alpha=0.2)
# Generate points within a torus
npoints = 1000
R = 1.0
r = 0.1
points = rand_torus(R, r, npoints)
torus_vol = 2. * math.pi**2 * R * r**2
# Determine bounding ellipsoids
pointvol = torus_vol / npoints
ells = nestle.bounding_ellipsoids(points, pointvol=pointvol)
# plot
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10., 10.))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
ax.scatter(points[:, 0], points[:, 1], points[:, 2], c='k', marker='.')
for ell in ells:
plot_ellipsoid_3d(ell, ax)
ax.set_xlim(-1., 1.)
ax.set_ylim(-1., 1.)
ax.set_zlim(-1., 1.)
ax.set_aspect('equal')
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
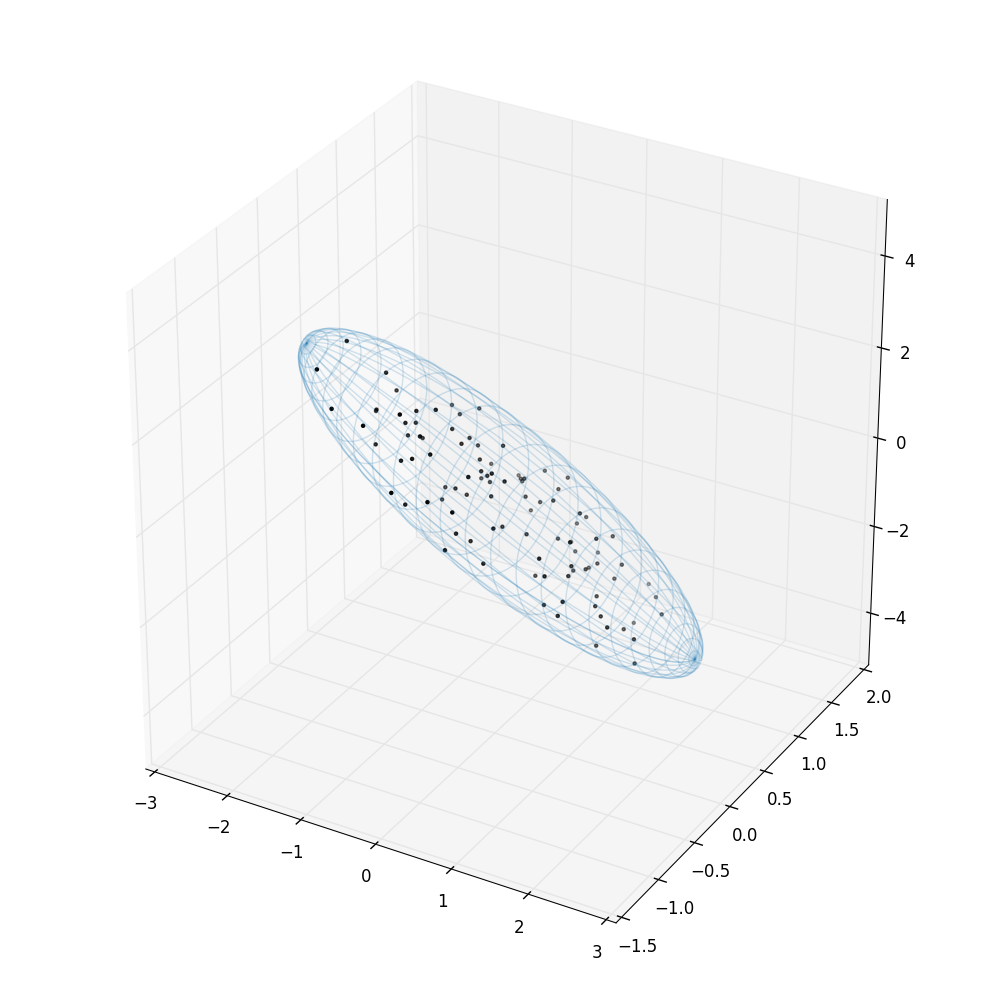
Single ellipsoid
Nestle correctly identifies a cloud of points as belonging to a single ellipsoid.
# Generate samples drawn from a single ellipsoid
npoints = 100
A = np.array([[0.25, 1., 0.5],
[1., 0.25, 0.5],
[0.5, 1., 0.25]])
ell_gen = nestle.Ellipsoid([0., 0., 0.], np.dot(A.T, A))
points = ell_gen.samples(npoints)
pointvol = ell_gen.vol / npoints
# Find bounding ellipsoid(s)
ells = nestle.bounding_ellipsoids(points, pointvol)
# plot
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10., 10.))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
ax.scatter(points[:, 0], points[:, 1], points[:, 2], c='k', marker='.')
for ell in ells:
plot_ellipsoid_3d(ell, ax)
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.307 seconds)